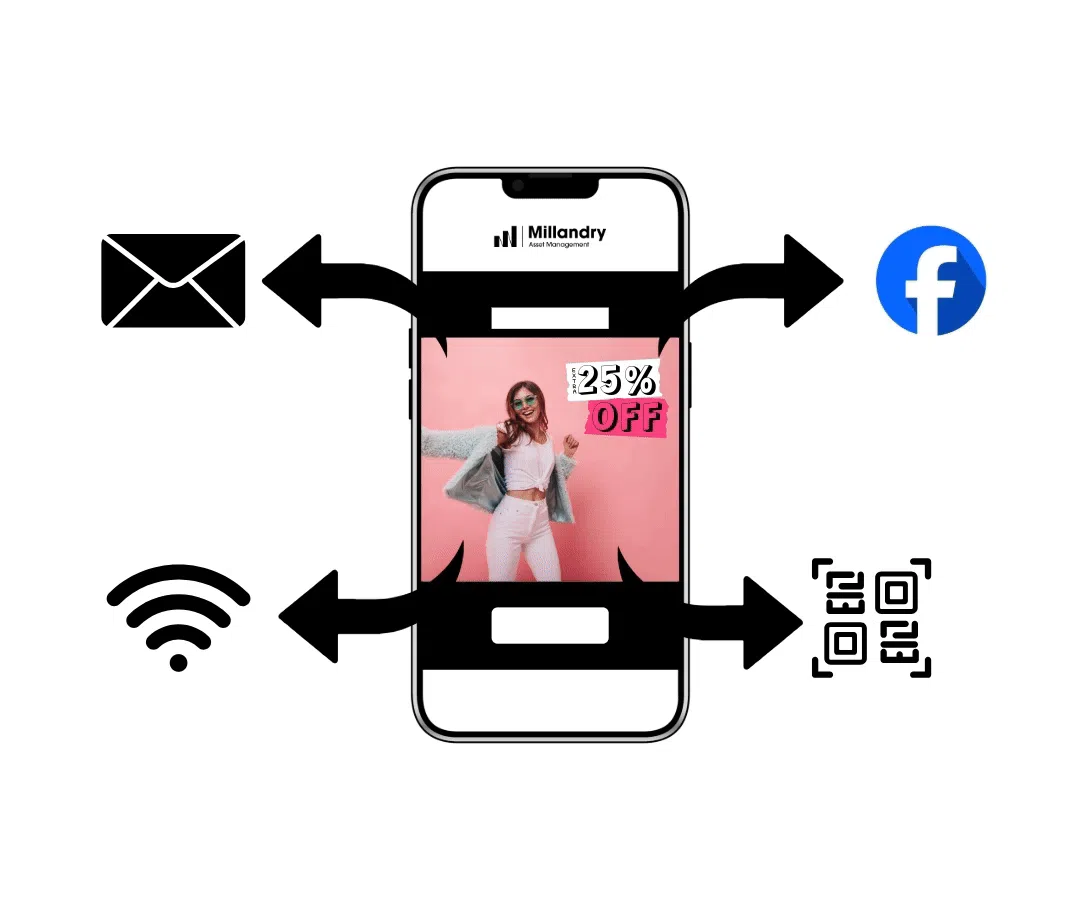
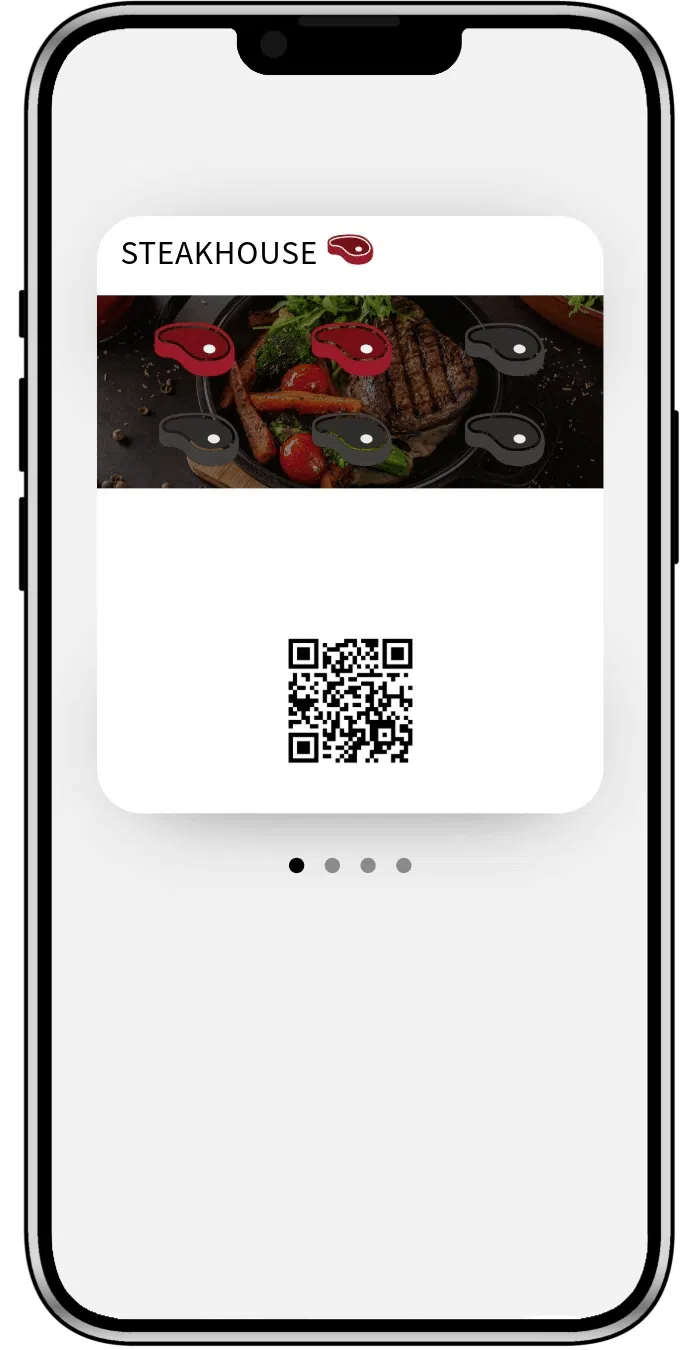
Conventional Processing


Understanding Conventional Processing
Conventional Processing:
An Overview
Conventional processing refers to the traditional methods used in various industries to transform raw materials into finished products. While modern technologies have introduced more automated and efficient techniques, conventional processing remains an integral part of many sectors, particularly where simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and reliability are paramount.
Key Characteristics of Conventional Processing:
1. Manual Labor: Conventional processing often involves a significant amount of human input and skilled labor. Workers may manually operate machines, monitor production lines, or carry out quality control processes.
2. Established Techniques: The techniques used in conventional processing have been tried and tested over decades, often evolving slowly but consistently to improve efficiency and product quality.
3. Less Automation: Unlike modern automated systems, conventional processing relies less on computer-controlled systems. This can result in longer production times but also allows for greater flexibility in certain operations.
4. Lower Capital Investment: Because conventional processing systems tend to be simpler, they generally require lower initial capital investment compared to newer, highly automated machinery.
Applications of Conventional Processing:
Manufacturing: In industries like textiles, paper, and metalworking, conventional processing methods such as milling, casting, and forging are still widely used due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness. Manufacturing: In industries like textiles, paper, and metalworking, conventional processing methods such as milling, casting, and forging are still widely used due to their versatility and cost-effectiveness.
Agriculture: Farming practices like crop harvesting, drying, and processing of grains are often done using conventional methods, which are affordable and well-understood.
Food Industry: Many traditional food processing techniques, such as fermentation, drying, and pickling, are still highly valued for producing artisanal and locally sourced foods.
Benefits of Conventional Processing:
Proven Reliability: Conventional methods have stood the test of time and are often reliable even in demanding environments.
Flexibility: These methods allow for easy adjustments in production processes to accommodate different materials or small-batch production runs.
Lower Maintenance Costs: Compared to highly automated systems, conventional machines typically have fewer complex components, which reduces the cost of maintenance and repairs.
Why Choose Conventional Processing?
While newer technologies can offer improved efficiency and precision, conventional processing is still a choice for many businesses due to its simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and familiarity. In sectors where precision is not the primary concern or when small-scale production is required, conventional methods can provide a sustainable and effective solution.
Mutual Growth, Mutual Success.
FOLLOW US:
COMPANY
CUSTOMER CARE
LEGAL
Mutual Growth, Mutual Success.
FOLLOW US
COMPANY
CUSTOMER CARE
LEGAL
Copyright 2025. Merchant Nations Association. All Rights Reserved.
Merchant Nation Association is a Registered MSP/ISO of Elavon, Inc. Georgia